Google My Business Profile - Optimizing Your Images in 2026
Jan 20, 2026
1. Introduction: The Death of the Digital Directory
The digital landscape for local commerce has reached a definitive turning point. For over a decade, the Google Business Profile (GBP) functioned as a text-based digital directory where ranking was primarily a matter of address accuracy and keyword density. By 2026, this model is obsolete.
The transition from the legacy "Google My Business" to a Gemini-powered discovery engine has redefined the profile as a "Visual Entity." In this new era of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), the quality, authenticity, and velocity of your visual data determine your visibility in the Local Map Pack and AI Overviews. To succeed today, businesses must move beyond static listings and embrace a strategy of Visual Authority.
2. The Geotagging "Poison Pill": Why Your Old Hacks are Hurting You
One of the most significant shifts in 2026 is the total debunking of manual EXIF geotagging. Once a staple of local SEO, injecting GPS coordinates into image metadata has become a "poison pill" that can actively damage a business's rankings.
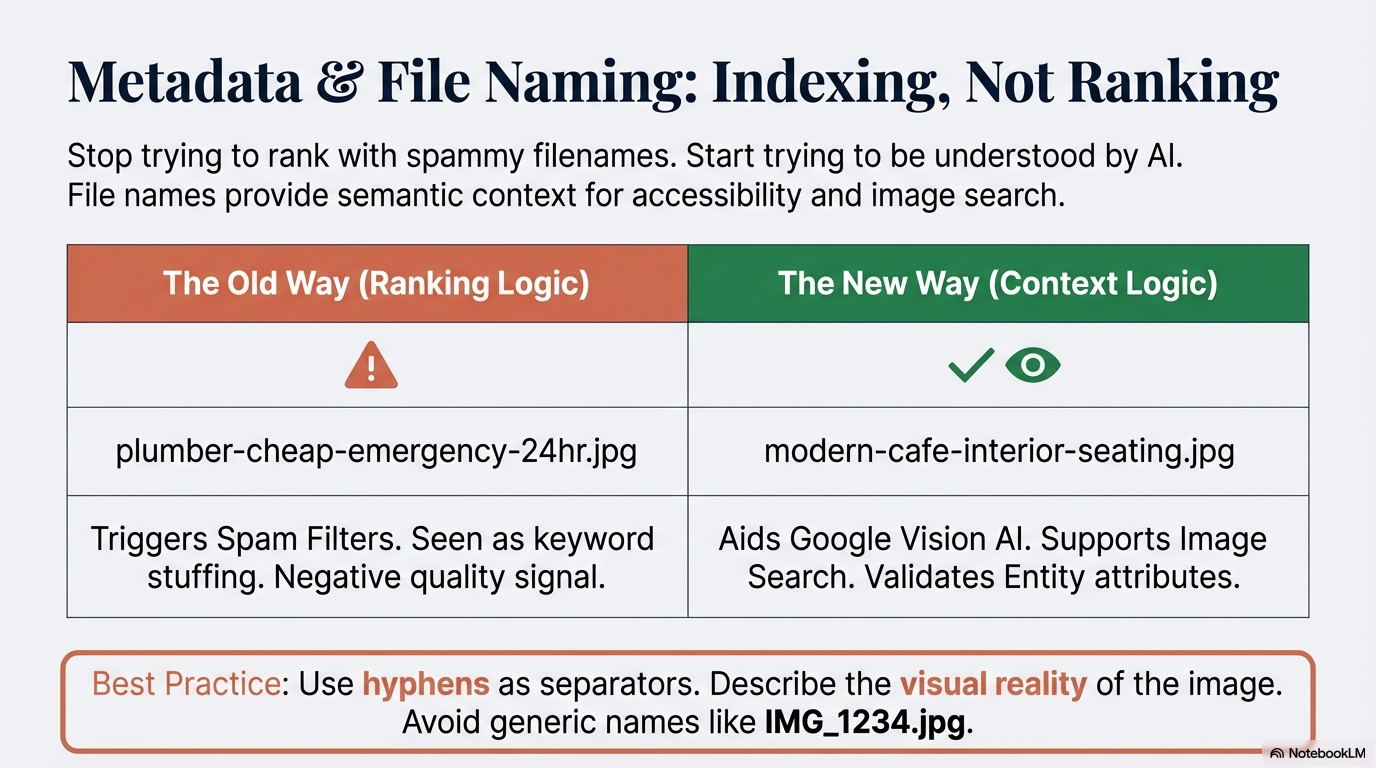
The Mechanism of Metadata Sanitization Google’s ingestion pipeline now includes a strict "Metadata Sanitization" process. For privacy and security reasons, Google strips all EXIF data—including latitude and longitude—immediately upon upload. As former Google insider Joel Headley explains:
"The 'tagging' is rendered irrelevant because the data does not persist in the serving layer of the image."
The Study of Diluted Authority A landmark 10-week study of 27 lawn care businesses revealed that geotagging is not just useless; it is detrimental. While the study showed a 97–98% statistical certainty of a minor lift for "near me" searches at the exact tagged coordinates, this came at a steep cost. The findings showed a "High Significance" decline in city-specific queries, home base visibility, and overall service area authority. By attempting to signal relevance in a distant location through metadata, businesses confuse the algorithm, leading to a loss of visibility at their actual verified address.
Technical Clarification: Schema vs. EXIF As a strategist, I must clarify that while EXIF geotagging is a liability, Schema markup on your website remains a valid and necessary signal for location. Furthermore, your file-naming strategy has shifted from a ranking lever to an indexing and accessibility tool. For 2026, ensure filenames use hyphens (not underscores) to ensure accurate parsing by crawlers and screen readers (e.g., modern-cafe-interior.jpg vs. modern_cafe_interior.jpg).
3. The End of "Perfect": Why Stock Photos and AI-Generated Visuals Fail
As generative AI floods the internet with synthetic imagery, a "trust deficit" has emerged. Google’s Vision AI models now prioritize "Visual Authenticity" to ensure search results represent reality.
- The Stock Photo Penalty: Google’s AI uses duplicate detection to instantly identify generic images. These are flagged as "non-unique" and relegated to the "By Owner" tab, where they receive minimal views.
- The "Skunk" Case Study: Entity mismatching can be catastrophic. When a lawn care business used a stock photo of a skunk to illustrate pest control, its ranking for the page dropped from #2 to #3. Google’s Vision AI associated the image with "animal removal" rather than "lawn care." Replacing the stock photo with a genuine, contextually relevant image restored the ranking.
- The Uncanny Valley and Regulation: As of August 2, 2026, C2PA (Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity) transparency regulations are strictly enforced. Google’s detection tools identify the lack of sensor noise typical of physical cameras. Consumers now punish perceived deception; AI-generated meals or storefronts act as a repellent in a marketplace that values the physical product.
4. Interaction Velocity: The New Algorithmic Heartbeat
In 2026, "Interaction Velocity"—the frequency and consistency of engagement and uploads—is a dominant ranking signal. Static "brochure" profiles signal a lack of relevance to AI models.
To maintain a healthy "algorithmic heartbeat," businesses should adopt a weekly upload cadence. This frequency allows the AI to ingest real-time data about the business's physical state and enables "Seasonal Relevance." For example, a coffee shop uploading images of "Pumpkin Spice Lattes" in October signals current relevance, triggering a boost for time-sensitive queries.
Furthermore, high-velocity profiles that include immersive media, such as 360° virtual tours, see an 87% increase in views. These tours significantly improve Dwell Time—a critical behavioral signal that tells the Gemini engine your listing is high-quality and worthy of a top-tier Map Pack position.
5. Images as Structured Data: The Rise of Visual Entity Recognition
Under the framework of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), images are no longer decorative; they are structured data containers used for visual validation.
Visual Entity Recognition When Google’s AI scans a profile, it seeks visual confirmation of text-based claims. If a restaurant claims to be "pet-friendly," the AI looks for photos of dogs on the patio to validate this claim. This "Entity Clarity" reduces friction in the Knowledge Graph and increases the likelihood of being featured in AI Overviews.
Multimodal Data Feeding The AI processes text, images, and video simultaneously. When a consistent narrative is maintained across all three formats, it reinforces the "truth" of the business entity, securing a stronger position in the search ecosystem.
6. The Camera is the New Keyboard: Optimizing for 100 Billion Visual Searches
With Google Lens and "Circle to Search" driving over 100 billion annual searches, the camera is effectively the new search bar.
- Subject Isolation: To capture visual search traffic, the main subject must be clear. Cluttered backgrounds confuse object recognition algorithms.
- Contextual Clarity and the "Price Tag" Tactic: For local retailers, showing a product in situ—specifically on the shelf with a visible price tag—helps Lens identify "Local Availability" intent.
- The Reseller Use Case: GBPs that maintain up-to-date visual inventories of unique items can attract high-intent foot traffic from users scanning objects in the real world and looking for local stock.

7. The Video Revolution and "Zero-Click" Engagement
Video content is now a non-negotiable requirement for GBP, driving engagement without the user ever visiting a website.
2026 Technical Constraints:
- Duration: Maximum 30 seconds.
- File Size: Maximum 75 MB.
- Resolution: Minimum 720p.
Strategic Applications:
- Intro Clips and YouTube Shorts: Short, unpolished, handheld videos of the owner build immediate rapport. Integrating YouTube Shorts allows high-authority video content to appear directly in your Knowledge Panel.
- Video Verification: This is now a primary tool to combat spam. New listings must often provide a continuous take showing the exterior, the entrance (unlocking the door), and the point-of-sale system.
- The Dilution Strategy: Managing bad User-Generated Content (UGC) is difficult in 2026. Because formal removal is slow, the most effective strategic counter-move is to "flood the zone" with high-quality, owner-verified content. Google’s display algorithm prioritizes recent, high-resolution owner photos, pushing negative or irrelevant UGC to the bottom of the feed.
8. Conclusion: Building Visual Authority
The era of "gaming" local search with hidden metadata and stock perfection has ended. In 2026, the roadmap to visibility is built on Visual Authority: the consistent delivery of authentic, high-frequency, and high-resolution visual data to the Knowledge Graph.
To lead in your market, you must cease the "poison pills" of manual geotagging and embrace a dynamic, video-first content strategy. As you evaluate your digital storefront, ask yourself: Does this profile reflect the physical truth of my business, or am I still hiding behind the facade of an outdated directory?


